What is it?
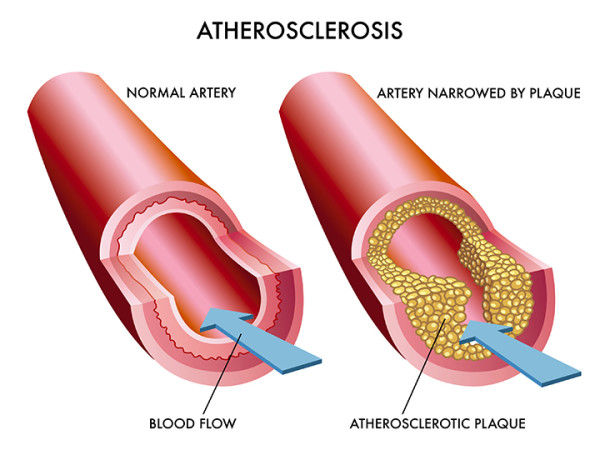
Atherosclerosis is a disease process leading to hardening and narrowing (stenosis) of your arteries. The buildup of fat, cholesterol, calcium and other substances creates plaques inside arteries, which can lead to serious problems including heart attack, stroke, amputation and death.
SERIOUS, POSSIBLE FATAL:
Atherosclerosis-related diseases are the No. 1 cause of death in the U.S. for both men and women. Roughly 5 million people in the U.S. are affected.
Preventable—even small changes can help:
Stopping smoking, following a healthy diet, managing cholesterol and staying physically active all decrease the risk of atherosclerosis and improve your overall health.
Symptoms
Until the arteries narrow significantly, many people experience no symptoms. Symptoms often appear only when the disease is advanced, and vary with the types of arteries affected.
Pain in the chest leading to angina or possibly a heart attack may indicate arteries of the heart are affected. Pain in the legs while walking may indicate arteries of the legs are affected.
A mini-stroke or stroke may occur if arteries of the neck are affected.
Causes
A variety of characteristics and behaviors called risk factors may contribute to atherosclerosis.
SOME RISK FACTORS CANNOT BE CHANGED:
Age, male gender, race and family history can put you at a higher risk.
• Smoking
• High blood pressure
• High amounts of cholesterol in the blood
• High amounts of sugar in the blood
• High levels of inflammation as the body responds to injury or infection
• Obesity
• Lack of physical activity
• Mental health issues
• Stress
Diagnosis
A vascular surgeon will ask questions about symptoms and medical history, including family history, and will perform a physical exam.
The vascular surgeon will likely recommend one or more a blood tests be done.
Depending on the arteries affected or suspected, additional tests may be recommended to understand the presence and severity of disease. These may include:
• Treadmill test
• Computed tomography (CT) scan
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
Treatment Options
• The vascular surgeon will provide information to help you understand the effects of atherosclerosis and may recommend changes in behavior or diet.
• Medications may be prescribed, for example, to manage high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
• If needed, surgery will be recommended and may include:
• Angioplasty or stenting
• Surgical bypass
Staying Healthy
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of atherosclerosis-related disease, primarily through lifestyle and dietary modifications that will improve your overall health.
• Stop smoking—ask your vascular surgeon to help you find a smoking cessation program that will work for you
• Improve nutrition through a balanced diet with reduced salt and fat
• Control blood pressure and sugar and cholesterol in the blood
• Maintain a healthy weight
• Manage stress
• Increase physical activity
The information contained on www.ntxvascular.com is sourced from the Society for Vascular Surgery at www.vascular.org. It is purely informational, and is not intended, nor should it be relied upon, as a substitute for the advice or treatment of a trained medical professional. Individuals with specific medical problems or questions must consult with their doctor or other health care professional.