What is it?
If you have CVI, valves in your veins (usually in the leg or sometimes the arms) don’t work, causing blood to pool in your legs and putting increased pressure on the walls of the veins. May be due to valve dysfunction (usually hereditary) or due to valve destruction after a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clot.
May affect up to 40% of the U.S population. More common in women (especially after multiple pregnancies) and in people who are middle-aged or older.
Even with very successful treatment, recurrence is common and you may need further care.
Symptoms
Most symptoms are mild, and not limb-threatening.
You may feel heaviness in the affected limb, as well as swelling and pain. Sometimes there is a darkening of the skin. An open sore or ulcer may develop—if your leg is affected, usually on the inside of the ankle—and it may be difficult to heal.
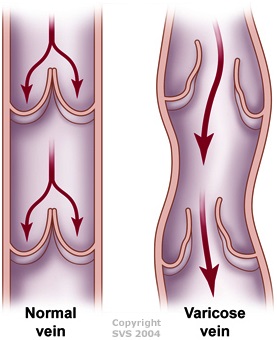
Enlarged and twisted veins close to the surface of the skin are a sign of a milder form of venous disease. You may feel burning, aching, heaviness and pain.
Causes
Vein valves become incompetent, especially when standing, for unknown reasons.
A blood clot in a deep vein that causes your vein valves to fail and may completely block the vein. This causes greater swelling and can lead to tissue changes that may cause darkening of the skin, dermatitis or ulcers.
Diagnosis
You will be asked questions about symptoms and medical history, including questions about family members. The vascular surgeon will also perform a physical exam.
• Duplex ultrasound testing to look at your vein valves and see if they work.
• In cases where severe swelling occurs and is difficult to treat, a computer tomography (CT) scan of the venous system to look for vein narrowing or blockage in your abdomen.
Treatment Options
Most treatment is nonsurgical. The main goal is to prevent severe swelling and ulcers from developing.
• Compression garments relieve symptoms and aid ulcer healing.
• If superficial veins are affected, they may be treated through vein ablation or injection.
• If varicose veins develop and are close to the skin, they may be removed through superficial vein stripping, usually an outpatient procedure.
• If deep veins are affected, in severe cases angioplasty and stenting may be recommended.
• In rare cases, surgical bypass may be required.
Staying Healthy
Here are ways to slow the progression of carotid artery disease:
• Maintain a normal weight
• Exercise regularly
• Wear compression garments
• Maintain good skin care
• If you have had a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), it is essential to stick with any anti-coagulation medications you have been prescribed Ask your vascular surgeon about medications that may help control the disease, including medications that can reduce your blood pressure and blood cholesterol, and make your blood less sticky.
The information contained on www.ntxvascular.com is sourced from the Society for Vascular Surgery at www.vascular.org. It is purely informational, and is not intended, nor should it be relied upon, as a substitute for the advice or treatment of a trained medical professional. Individuals with specific medical problems or questions must consult with their doctor or other health care professional.